What is a tunnel diode?
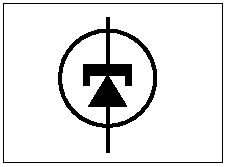
Dr.Leo Esaki invented a tunnel diode, which is also known as “Esaki
diode” on behalf of its inventor. Its a high conductivity two terminal
P-N junction diode doped heavily about 1000 times greater than a
conventional junction diode. Because of heavy doping depletion layer
width is reduced to an extremely small value of 1/10000 m. Reverse
breakdown voltage is also reduced to very small value~0 resulting in
appearance of the diode to be broken for any reverse voltage and a
negetive resistance section is produced in the volt-ampere
characteristics of the diode.
What is tunneling in a tunnel diode?
Through the reduced depletion layer,it can result in careers
“punching through” the junction with velocity of light,even when they
have no energy to cross potential barrier. As a result a large forward
current is produced at relatively low forward voltage(<100mv). Such a
mechanism of conduction in which charge carriers punch through the
junction is “tunneling”. Because of heavy doping a tunnel diode cam
conduct in both directions but it is usually used for forward conduction
only.
Construction of a tunnel diode:
Tunnel diodes are usually fabricated from germanium,gallium arsenide,
or gallium antimonide. Silicon is not used in the construction of
tunnel diode becuase Ip/Iv is maximum in case of Gallium
arsenide.(Ip=Peak value of forward current and Iv= Valley current). This
ratio is very small for silicon and is of the order of 3. Ordinarily
they are manufatured by alloying from gallium arsenide. Source materials
are highly doped semiconductor crystals with an impurity concentration
of the order 10^25 per cubic meter.
Note: Being a low power device a tunnel diode can be damaged easily by heat and static electricity.
Tunnel Diode Characteristics is shown below:


No comments:
Post a Comment