This article is about how to interface a seven segment LED display to an
8051 microcontroller. 7 segment LED display is very popular and it can
display digits from 0 to 9 and quite a few characters like A, b, C, .,
H, E, e, F, n, o,t,u,y, etc. Knowledge about how to interface a seven
segment display to a micro controller is very essential in designing
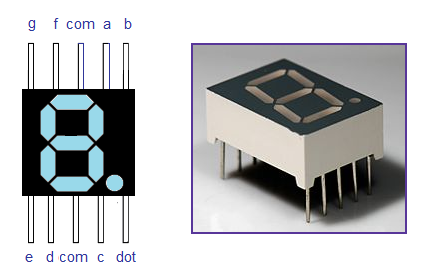
embedded systems. A seven segment display consists of seven LEDs
arranged in the form of a squarish ’8′ slightly
inclined to the right and a single LED as the dot character. Different
characters can be displayed by selectively glowing the required LED
segments. Seven segment displays are of two types, common cathode and common anode. In common cathode type , the cathode of all LEDs are tied together to a single terminal which is usually labeled as ‘com‘
and the anode of all LEDs are left alone as individual pins labeled
as a, b, c, d, e, f, g & h (or dot) . In common anode type, the
anode of all LEDs are tied together as a single terminal and cathodes
are left alone as individual pins. The pin out scheme and picture of a
typical 7 segment LED display is shown in the image below.
 |
| 7 segment LED display |
Digit drive pattern.
Digit drive pattern of a seven segment LED display is simply the different logic combinations of its terminals ‘a’ to ‘h‘
in order to display different digits and characters. The common digit
drive patterns (0 to 9) of a seven segment display are shown in the
table below.
 |
| Interfacing 7 segment display to 8051 |
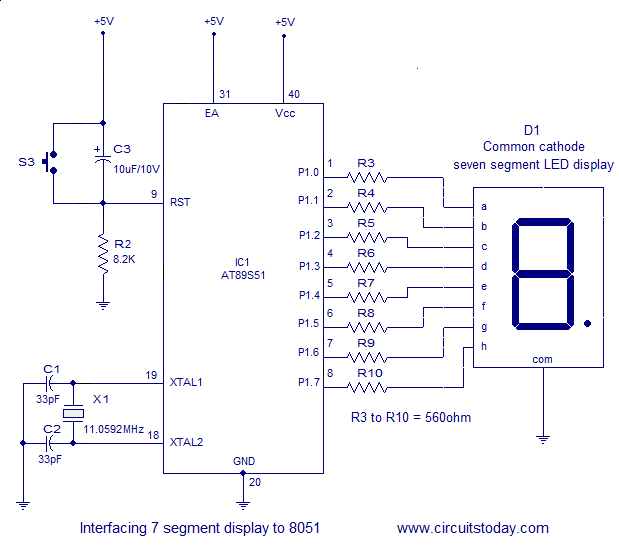
The circuit diagram shown above is of an
AT89S51 microcontroller based 0 to 9 counter which has a 7 segment LED
display interfaced to it in order to display the count. This simple
circuit illustrates two things. How to setup simple 0 to 9 up counter
using 8051 and more importantly how to interface a seven segment LED
display to 8051 in order to display a particular result. The common
cathode seven segment display D1 is connected to the Port 1 of the
microcontroller (AT89S51) as shown in the circuit diagram. R3 to R10 are
current limiting resistors. S3 is the reset switch and R2,C3 forms a
debouncing circuitry. C1, C2 and X1 are related to the clock circuit.
The software part of the project has to do the following tasks.
- Form a 0 to 9 counter with a predetermined delay (around 1/2 second here).
- Convert the current count into digit drive pattern.
- Put the current digit drive pattern into a port for displaying.
All the above said tasks are accomplished by the program given below.
Program.
ORG 000H //initial starting address
START: MOV A,#00001001B // initial value of accumulator
MOV B,A
MOV R0,#0AH //Register R0 initialized as counter which counts from 10 to 0
LABEL: MOV A,B
INC A
MOV B,A
MOVC A,@A+PC // adds the byte in A to the program counters address
MOV P1,A
ACALL DELAY // calls the delay of the timer
DEC R0//Counter R0 decremented by 1
MOV A,R0 // R0 moved to accumulator to check if it is zero in next instruction.
JZ START //Checks accumulator for zero and jumps to START. Done to check if counting has been finished.
SJMP LABEL
DB 3FH // digit drive pattern for 0
DB 06H // digit drive pattern for 1
DB 5BH // digit drive pattern for 2
DB 4FH // digit drive pattern for 3
DB 66H // digit drive pattern for 4
DB 6DH // digit drive pattern for 5
DB 7DH // digit drive pattern for 6
DB 07H // digit drive pattern for 7
DB 7FH // digit drive pattern for 8
DB 6FH // digit drive pattern for 9
DELAY: MOV R4,#05H // subroutine for delay
WAIT1: MOV R3,#00H
WAIT2: MOV R2,#00H
WAIT3: DJNZ R2,WAIT3
DJNZ R3,WAIT2
DJNZ R4,WAIT1
RET
ENDAbout the program.
Instruction MOVC A,@A+PC is the
instruction that produces the required digit drive pattern for the
display. Execution of this instruction will add the value in the
accumulator A with the content of the program counter(address of the
next instruction) and will move the data present in the resultant
address to A. After this the program resumes from the line after MOVC
A,@A+PC.
In the program, initial value in A is
00001001B. Execution of MOVC A,@A+PC will add oooo1001B to the content
in PC ( address of next instruction). The result will be the address
of command DB 3FH (line15) and the data present in this address ie 3FH
(digit drive pattern for 0) gets moved into the accumulator. Moving this
pattern in the accumulator to Port 1 will display 0 which is the first
count.
At the next count, value in A will
advance to 00001010 and after the execution of MOVC A,@+PC ,the value
in A will be 06H which is the digit drive pattern for 1 and this will
display 1 which is the next count and this cycle gets repeated for
subsequent counts.
The reason why accumulator is loaded
with 00001001B (9 in decimal) initially is that the instructions from
line 9 to line 15 consumes 9 bytes in total.
The lines 15 to 24 in the program which starts with command DB can be called as a Look Up Table (LUT).
Command DB is known as Define Byte – which defines a byte. This table
defines the digit drive patterns for 7 segment display as bytes (in hex
format). MOVC operator fetches the byte from this table based on the
result of adding PC and contents in the accumulator.
Register B is used as a temporary
storage of the initial value of the accumulator and the subsequent
increments made to accumulator to fetch each digit drive pattern one by
one from the look up table(LUT).
Note:- In line 6,
Accumulator is incremented by 1 each time (each loop iteration) to
select the next digit drive pattern. Since MOVC operator uses the value
in A to fetch the digit drive pattern from LUT, value in ACC has to be
incremented/manipulated accordingly. The digit drive patterns are
arranged consecutively in LUT.
Register R0 is used as a counter which
counts from 10 down to 0. This ensures that digits from o to 9 are
continuously displayed in the 7 segment LED. You may note lines 4, 11,
12, and 13 in the above program. Line 4 initializes R0 to 10 (OAh). When
the program counter reaches line 11 for the first time, 7 segment LED
has already displayed 0. So we can reduce one count and that is why we
have written DEC Ro. We need to continuously check if R0 has reached
full count (that is 0). In order to do that lines 12 and 13 are used. We
move R0 to accumulator and then use the Jump if Zero (JZ) instruction
to check if accumulator has reached zero. If Acc=0, then we makes the
program to jump to START (initial state) and hence we restart the 7
segment LED to display from 0 to 9 again. If Acc not equal to zero, we
continue the program to display the next digit (check line 14).
Interfacing Seven segment display to 8051
A Note about 7 segment LED display.
This article is about how to interface a
seven segment LED display to an 8051 microcontroller. 7 segment LED
display is very popular and it can display digits from 0 to 9 and quite
a few characters like A, b, C, ., H, E, e, F, n, o,t,u,y, etc.
Knowledge about how to interface a seven segment display to a micro
controller is very essential in designing embedded systems. A seven
segment display consists of seven LEDs arranged in the form of a
squarish ’8′ slightly inclined to the right and a
single LED as the dot character. Different characters can be displayed
by selectively glowing the required LED segments. Seven segment displays
are of two types, common cathode and common anode. In common cathode type , the cathode of all LEDs are tied together to a single terminal which is usually labeled as ‘com‘
and the anode of all LEDs are left alone as individual pins labeled
as a, b, c, d, e, f, g & h (or dot) . In common anode type, the
anode of all LEDs are tied together as a single terminal and cathodes
are left alone as individual pins. The pin out scheme and picture of a
typical 7 segment LED display is shown in the image below.
Digit drive pattern.
Digit drive pattern of a seven segment LED display is simply the different logic combinations of its terminals ‘a’ to ‘h‘
in order to display different digits and characters. The common digit
drive patterns (0 to 9) of a seven segment display are shown in the
table below.
| Digit | a | b | c | d | e | f | g |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Interfacing seven segment display to 8051.
The circuit diagram shown above is of an
AT89S51 microcontroller based 0 to 9 counter which has a 7 segment LED
display interfaced to it in order to display the count. This simple
circuit illustrates two things. How to setup simple 0 to 9 up counter
using 8051 and more importantly how to interface a seven segment LED
display to 8051 in order to display a particular result. The common
cathode seven segment display D1 is connected to the Port 1 of the
microcontroller (AT89S51) as shown in the circuit diagram. R3 to R10 are
current limiting resistors. S3 is the reset switch and R2,C3 forms a
debouncing circuitry. C1, C2 and X1 are related to the clock circuit.
The software part of the project has to do the following tasks.
- Form a 0 to 9 counter with a predetermined delay (around 1/2 second here).
- Convert the current count into digit drive pattern.
- Put the current digit drive pattern into a port for displaying.
All the above said tasks are accomplished by the program given below.
Program.
ORG 000H //initial starting address
START: MOV A,#00001001B // initial value of accumulator
MOV B,A
MOV R0,#0AH //Register R0 initialized as counter which counts from 10 to 0
LABEL: MOV A,B
INC A
MOV B,A
MOVC A,@A+PC // adds the byte in A to the program counters address
MOV P1,A
ACALL DELAY // calls the delay of the timer
DEC R0//Counter R0 decremented by 1
MOV A,R0 // R0 moved to accumulator to check if it is zero in next instruction.
JZ START //Checks accumulator for zero and jumps to START. Done to check if counting has been finished.
SJMP LABEL
DB 3FH // digit drive pattern for 0
DB 06H // digit drive pattern for 1
DB 5BH // digit drive pattern for 2
DB 4FH // digit drive pattern for 3
DB 66H // digit drive pattern for 4
DB 6DH // digit drive pattern for 5
DB 7DH // digit drive pattern for 6
DB 07H // digit drive pattern for 7
DB 7FH // digit drive pattern for 8
DB 6FH // digit drive pattern for 9
DELAY: MOV R4,#05H // subroutine for delay
WAIT1: MOV R3,#00H
WAIT2: MOV R2,#00H
WAIT3: DJNZ R2,WAIT3
DJNZ R3,WAIT2
DJNZ R4,WAIT1
RET
ENDAbout the program.
Instruction MOVC A,@A+PC is the
instruction that produces the required digit drive pattern for the
display. Execution of this instruction will add the value in the
accumulator A with the content of the program counter(address of the
next instruction) and will move the data present in the resultant
address to A. After this the program resumes from the line after MOVC
A,@A+PC.
In the program, initial value in A is
00001001B. Execution of MOVC A,@A+PC will add oooo1001B to the content
in PC ( address of next instruction). The result will be the address
of command DB 3FH (line15) and the data present in this address ie 3FH
(digit drive pattern for 0) gets moved into the accumulator. Moving this
pattern in the accumulator to Port 1 will display 0 which is the first
count.
At the next count, value in A will
advance to 00001010 and after the execution of MOVC A,@+PC ,the value
in A will be 06H which is the digit drive pattern for 1 and this will
display 1 which is the next count and this cycle gets repeated for
subsequent counts.
The reason why accumulator is loaded
with 00001001B (9 in decimal) initially is that the instructions from
line 9 to line 15 consumes 9 bytes in total.
The lines 15 to 24 in the program which starts with command DB can be called as a Look Up Table (LUT).
Command DB is known as Define Byte – which defines a byte. This table
defines the digit drive patterns for 7 segment display as bytes (in hex
format). MOVC operator fetches the byte from this table based on the
result of adding PC and contents in the accumulator.
Register B is used as a temporary
storage of the initial value of the accumulator and the subsequent
increments made to accumulator to fetch each digit drive pattern one by
one from the look up table(LUT).
Note:- In line 6,
Accumulator is incremented by 1 each time (each loop iteration) to
select the next digit drive pattern. Since MOVC operator uses the value
in A to fetch the digit drive pattern from LUT, value in ACC has to be
incremented/manipulated accordingly. The digit drive patterns are
arranged consecutively in LUT.
Register R0 is used as a counter which
counts from 10 down to 0. This ensures that digits from o to 9 are
continuously displayed in the 7 segment LED. You may note lines 4, 11,
12, and 13 in the above program. Line 4 initializes R0 to 10 (OAh). When
the program counter reaches line 11 for the first time, 7 segment LED
has already displayed 0. So we can reduce one count and that is why we
have written DEC Ro. We need to continuously check if R0 has reached
full count (that is 0). In order to do that lines 12 and 13 are used. We
move R0 to accumulator and then use the Jump if Zero (JZ) instruction
to check if accumulator has reached zero. If Acc=0, then we makes the
program to jump to START (initial state) and hence we restart the 7
segment LED to display from 0 to 9 again. If Acc not equal to zero, we
continue the program to display the next digit (check line 14).
Multiplexing 7 segment display to 8051.
Suppose you need a three digit display
connected to the 8051. Each 7 segment display have 8 pins and so a total
amount of 24 pins are to the connected to the microcontroller and there
will be only 8 pins left with the microcontroller for other input
output applications. Also the maximum number of displays that can be
connected to the 8051 is limited to 4 because 8051 has only 4 ports.
More over three 3 displays will be ON always and this consumes a
considerable amount of power. All these problems associated with the
straight forward method can be solved by multiplexing .
In multiplexing all displays are
connected in parallel to one port and only one display is allowed to
turn ON at a time, for a short period. This cycle is repeated for at a
fast rate and due to the persistence of vision of human eye, all digits
seems to glow. The main advantages of this method are
- Fewer number of port pins are required .
- Consumes less power.
- More number of display units can be interfaced (maximum 24).
The circuit diagram for multiplexing 2 seven segment displays to the 8051 is shown below.
 |
| Multiplexing 7 segement display to 8051 |
When assembled and powered on, the
circuit will display the number ’16′ and let us see how it is done.
Initially the first display is activated by making P3.0 high and then
digit drive pattern for “1″ is loaded to the Port 1. This will make the
first display to show “1″. In the mean time P3.1 will be low and so do
the second display will be OFF. This condition is maintained for around
1ms and then P3.0 is made low. Now both displays will be OFF. Then the
second display is activated by making P3.1 high and then the digit drive
pattern for “6″ is loaded to the port 1. This will make the second
display to show “6″. In the mean time P3.0 will be low and so the second
display will be OFF. This condition is maintained for another 1ms and
then port 3.1 is made low. This cycle is repeated and due to the
persistence of vision you will feel it as “16″.
Transistor Q1 drives the first display
(D1) and transistor Q2 drives the second display (D2). R11 and R12 are
the base current limiting resistors of Q1 and Q2. The purpose of other
components are explained in the first circuit.
Program.
ORG 000H // initial starting address
MOV P1,#00000000B // clears port 1
MOV R6,#1H // stores "1"
MOV R7,#6H // stores "6"
MOV P3,#00000000B // clears port 3
MOV DPTR,#LABEL1 // loads the adress of line 29 to DPTR
MAIN: MOV A,R6 // "1" is moved to accumulator
SETB P3.0 // activates 1st display
ACALL DISPLAY // calls the display sub routine for getting the pattern for "1"
MOV P1,A // moves the pattern for "1" into port 1
ACALL DELAY // calls the 1ms delay
CLR P3.0 // deactivates the 1st display
MOV A,R7 // "2" is moved to accumulator
SETB P3.1 // activates 2nd display
ACALL DISPLAY // calls the display sub routine for getting the pattern for "2"
MOV P1,A // moves the pattern for "2" into port 1
ACALL DELAY // calls the 1ms delay
CLR P3.1 // deactivates the 2nd display
SJMP MAIN // jumps back to main and cycle is repeated
DELAY: MOV R3,#02H
DEL1: MOV R2,#0FAH
DEL2: DJNZ R2,DEL2
DJNZ R3,DEL1
RET
DISPLAY: MOVC A,@A+DPTR // adds the byte in A to the address in DPTR and loads A with data present in the resultant address
RET
LABEL1:DB 3FH
DB 06H
DB 5BH
DB 4FH
DB 66H
DB 6DH
DB 7DH
DB 07H
DB 7FH
DB 6FH
END

No comments:
Post a Comment